China's education system
Updated: 2017-12-12 (chinadaily.com.cn)  Print
Print 

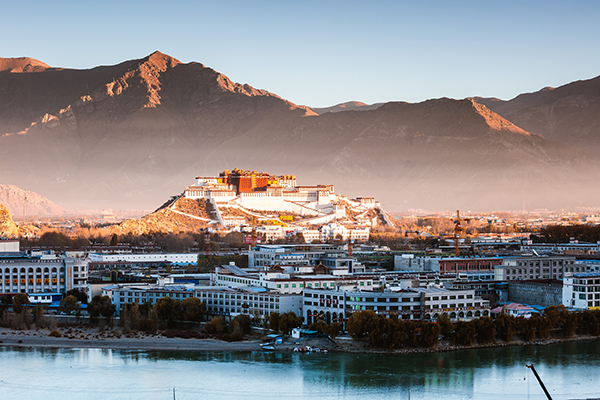
China's education system is divided into 4 categories: basic education, occupational/polytechnic education, higher education and adult education.
Basic Education
Basic education consists of pre-school education, primary (6 years) and junior (3 years) and senior (3 years) middle school.
The Chinese government has always viewed basic education as one of its top priorities. Since 1986, when the Law of Compulsory Education of the People's Republic of China was promulgated, primary schooling has become available in most areas in China, while junior middle schooling has become widely available in large cities and economically developed areas. In 1999, the enrollment rate of school-age children reached 99.09% - 135.5 million children - and there were 582,300 primary schools around the country.
Also in 1999, there were 64,400 common junior middle schools around China, with enrollment of 58.1 million pupils. There were also 14,100 common high schools nationwide with an enrollment of 10.4 million. In 1998, there were 10,074 occupational middle schools nationwide with an enrollment of 5.416 million.
In 1999, there were 1,520 special schools for the hearing-impaired and also for mentally disabled children, with an enrollment of 371,600. More than half of the country's children with some sort of disability had access to basic education. There were also 181,110 kindergartens nationwide in 1999, with an enrollment of 23.2 million..
Medium-level Occupational and Polytechnic Education
This category consists of medium-level professional schools, polytechnic schools, occupational middle schools as well as various short-term occupational and technical training programs.
Since the 1980's, China's occupational and polytechnic education has experienced rapid development. In 1997, there were 33,464 occupational and polytechnic schools nationwide with an enrollment of 18.6 million. The same year, there were more than 2,100 training schools training about 1 million students per year. The proportion of enrollment of high-school-equivalent occupational and polytechnic schools out of the total enrollment of China's high schools increased from 18.9% in 1980 to 56.47% in 1999.
In 1999, there were 3,962 secondary technical schools nationwide, with an enrollment of 5,155,000, and the number of those enrolled in finance and economics, sports and arts programs increased steadily, while the enrollment in technical subjects gradually decreased. In 1999, there were 8,317 vocational senior middle schools nationwide with enrollment reaching 4,438,400, and 4,098 polytechnic schools with an enrollment of 1,560,500.








