The archaeological excavation project of the Qingchi site has recently made significant archaeological discoveries. It marks the first time that transitional remains from the Neolithic to the Paleolithic era have been discovered.
The Qingchi site is located in Zhouhewan town, Jizhou district, Tianjin. The Tianjin archaeological department conducted three archaeological excavations at the site in the 1990s, revealing remains from the Neolithic and Xia-Shang-Zhou periods (2100-256 BC).
In 2015, the Tianjin Cultural Heritage Protection Center conducted a reexamination of the Qingchi site and discovered clues indicating the distribution of remains from the Paleolithic era.
From October to December 2023, a fourth archaeological excavation of the Qingchi site was conducted with the approval of the National Cultural Heritage Administration. Within two excavation areas, late Paleolithic stratigraphic sequences and transitional remains from the Paleolithic to the Neolithic era were uncovered. Over 1,000 cultural artifacts of various materials, including stone tools, ground stone tools, pottery, bone artifacts, and animal bones, were unearthed.
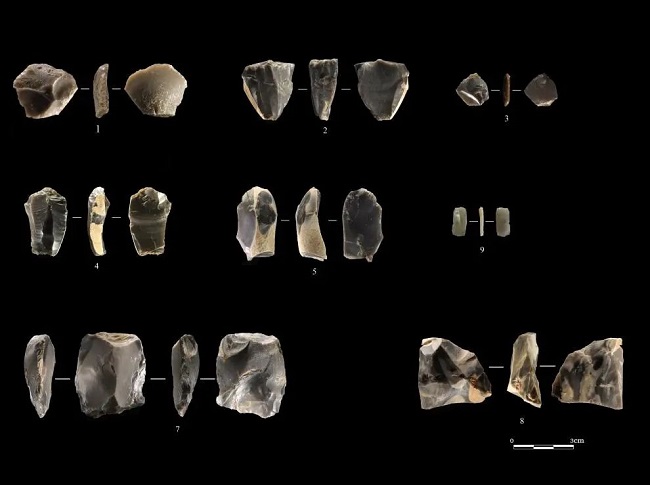
The Artifacts (Paleolithic) unearthed from the first excavation area of the Qingchi site [Photo provided by the Tianjin Cultural Heritage Conservation Center]
Sheng Lishuang, the project leader of the archaeological excavation at the Qingchi site, introduced that Paleolithic remains were discovered in the first excavation area of the site. Based on the excavated artifacts, geological environment, and other comprehensive inferences, the age of the Paleolithic remains is estimated to be between 40,000 and 10,000 years ago, corresponding to the late Paleolithic era.
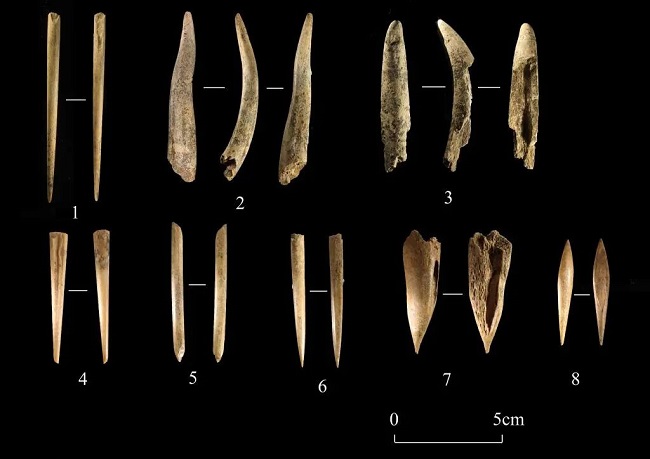

The Artifacts (Neolithic) unearthed from the second excavation area of the Qingchi site [Photo provided by the Tianjin Cultural Heritage Conservation Center]
Sheng also stated that in the second excavation area of the Qingchi site, remains from the Neolithic era were uncovered, breaking the stratigraphic relationship with the Paleolithic era. Based on the cultural characteristics of the excavated pottery and previous dating data, it has been determined that the lowermost layer dates back to the early Neolithic era, approximately 8,000 to 10,000 years ago.
Sheng further mentioned that the current archaeological excavation indicates the transitional characteristics of diverse production and livelihood methods during that period.





