Investment environment
As the capital city of Northwest China’s Gansu Province and an important city on the Silk Road Economic Belt, Lanzhou has a great potential for attracting investment.
Social-economic development of Lanzhou during the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-2020)
Basic information
Affected by the downward pressure on international and domestic economies, the economic development in Lanzhou during the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-2020) has turned from high-speed growth to steady growth.
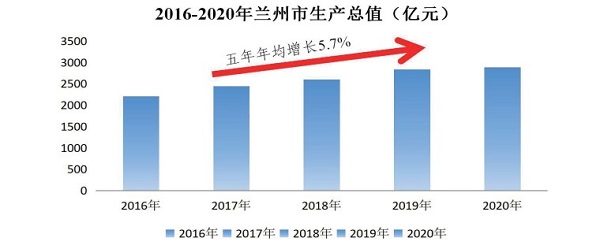
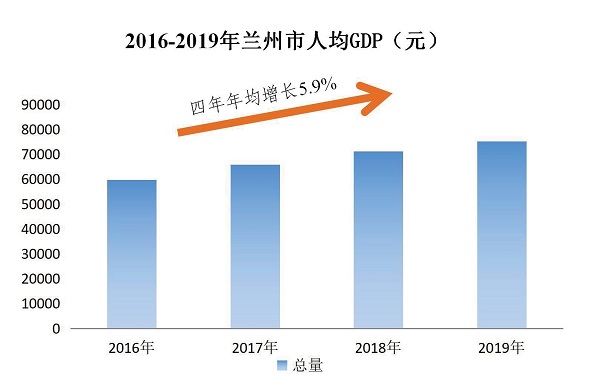
In late 2020, the regional GDP of Lanzhou was 288.7 billion yuan (US $44,629 million), 1.4 times the figure at the end of the 12th Five-Year Plan period (2011-15), with an average annual growth rate of 5.7% over the past five years, accounting for 32% of the whole province’s GDP. The GDP per capita of Lanzhou increased from 57,142 yuan (US $8,834.2) in 2015 to 75,217 yuan (US $11,628.6) in 2019 with an average annual growth of 5.9%.
Industrial upgrading
Since the start of the 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020), Lanzhou has continuously adjusted its structure of investment, enabling it to play a major role in supporting economic growth and guiding the economy to gradually shift to a new stage of development that improves quality and increases benefit.
At the end of the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-2020), fixed asset investment increased by 3.4%, and industrial investment increased by 26.0%. The investment structure of the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors has changed with increases in the primary and tertiary sectors.
Market consumption
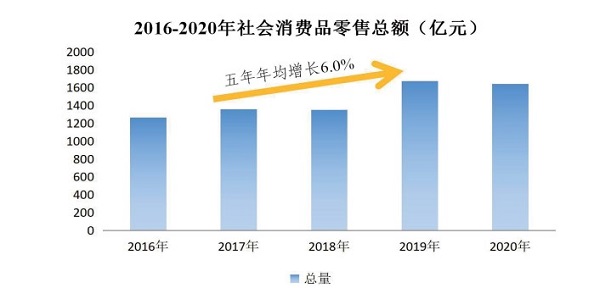
Lanzhou’s total retail sales of consumer goods in late 2020 increased by 1.4 times year-on-year to 164.1 billion yuan (US $25.4 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 6.0% over the five years. Urban and rural consumption increased year by year with urban retail sales expanding from 97.2 billion yuan (US $15 billion) to 143.9 billion yuan (US $22.3 billion) at an average annual growth rate of 6.1%.
Banking & Finance
Lanzhou’s financial industry, as the core of the modern economy, has never stopped reforming and innovating. Its ability to serve the real economy has been improving and the capital market has been active.
Lanzhou’s financial institutions’ balance of deposits in local and foreign currencies increased by 1.1 times year-on-year to 908.4 billion yuan (US $140.5 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 2.7% over the five years.
Lanzhou’s financial institutions’ balance of loans in local and foreign currencies increased by 1.8 times year-on-year to 1,316.7 billion yuan (US $203.7 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 12.7% over the five years.
The balance of RMB deposits increased by 1.2 times year-on-year to 904.5 billion yuan (US $139.9 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 3.0% over the five years. The balance of RMB loans increased by 1.9 times year-on-year to 1,295.5 billion yuan (US $200.4 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 13.5% over the five years.
Comprehensively, the added value of the financial industry increased from 24 billion yuan (US $3.7 billion) to 43.2 billion yuan (US $6.7 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 11.6%.
People’s livelihoods
During the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-2020), Lanzhou’s general public budget revenue increased from 18.5 billion yuan (US $2.9 billion) to 24.7 billion yuan (US $3.8 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 5.9%. The general public budget expenditure increased from 34.4 billion yuan (US $5.3 billion) to 48.6 billion yuan (US $7.5 billion) with an average annual growth rate of 7.1%.
Expenditures for people’s livelihoods have increased. The total allocations for education, culture, sports and media, social security and employment, health, agriculture, forestry and water are now 106.7 billion yuan (US $16.5 billion).
The per capita disposable income of urban and rural residents in Lanzhou is 40,152 yuan (US $6211.5) and 14,625 yuan (US $2262.5) with an average annual growth rate exceeding 8%.
The per capita consumption expenditure of urban residents increased from 20,156 yuan (US $3118.1) to 25,892 yuan (US $4005.5) and the per capita consumption expenditure of rural residents increased from 7,940 yuan (US $1228.3) to 11,551 yuan (US $1786.9).
Technical innovation
During the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-2020), Lanzhou’s scientific and technological innovation developed rapidly, keeping pace with economic development. In 2019, the city’s R&D investment was 6.392 billion yuan, ranking second among the five capital cities in the Northwest China. Three “Top 500” enterprises invested more than 60 projects.
Industrial distribution
Lanzhou’s main industries include: advanced petrochemicals, equipment manufacturing, biomedicals, green metallurgy, new materials, new energy, new building materials, energy conservation and environmental protection, food processing, digital information, modern service and modern agriculture.
Policy support
National strategies such as the Belt and Road Initiative, the go-west campaign, the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River basin, and the construction of urban agglomeration have given Lanzhou a number of major supportive policies.
The construction of Lanzhou New Area, the Lanzhou-Baiyin National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone, Lanzhou Yuzhong Ecological Innovation Zone, and the Yellow River Scenic Area provided investment opportunities.
Lanzhou’s late-comer advantages in opening-up and development are becoming increasingly prominent, and the overlapping opportunities it faces are unprecedented.
Copyright © Lanzhou City, Gansu Province.
All rights reserved. Presented by China Daily.
Copyright © Lanzhou City, Gansu Province. All rights reserved. Presented by China Daily.




