Innovation of Industrial Chains in China:Understanding, Cases and Discussions
Aug 12,2008
Chen Xiaohong & Chen Jinliang, Enterprise Research Institute of DRC
Research Report No.157, 2008
The innovation of industrial chains is a kind of innovation created by enterprise groups, that is, the enterprise groups that make up the industrial chains, by means of interaction and demand incentive or supply incentive, successively or jointly bring out new products or product combinations bearing an upstream-downstream relationship or being in harmony with one another. Studying the innovation of industrial chains is of great importance to the enhancement of the competitive edge of China's industries in the world.
I. Innovation of Industrial Chains in China: Advantages and Problems
1. Advantages
According to Michael Porter’s Diamond Model, the factors affecting the innovation of industrial chains mainly include industrial basis, market, production factors, enterprises and policy. In China, some of the factors are advantageous while others are disadvantageous or restrictive.
China has an integrated industrial system, a fairly favorable organizational basis for industrial technologies and economies as well as a good foundation for development, but lacks new technologies and management organizations and has little knowledge, experience and ability in combining technologies with commerce. China, being short of funds in the long run, has seen a quite inadequate knowledge accumulation in its industries where funds and technologies are a joint driving force for innovation.
China has advantages in terms of market. A large market favors the industrial chain innovation. But if foreign enterprises act swiftly to gain scale benefits, the Chinese domestic enterprises will then have much difficulty in acquiring market shares.
China has rich human resources, and its fund resources are on the increase as well. Nevertheless, there exists a shortage of high-quality talented people, and China’s ability to acquire and assess the information about the capital market is poor.
China has a number of enterprises with actual strength and sound mechanisms as well as a number of excellent entrepreneurs, which are the most important resources for China to realize the innovation of industrial chains. The main problem facing Chinese enterprises is that the enterprises are less capable of developing high technologies, acquiring and assessing strategic information and exercising organization and management and that they are less experienced in creating joint development and innovations.
As an important force to push forward innovation, the Chinese government has laid down the state strategy for innovation and development and formulated policies with a view to encouraging enterprises to make innovations. However, the government still needs to enrich its experience and improve its policy efficiency in order to give an impetus to the innovation under market economy.
Since 1980s, China has accumulated new experiences in innovation of industrial chains, which are different from those accumulated under planned economy. In terms of the relationship with the government, two basic forms are adopted in innovation making: innovations made through the co-operation between governments and enterprises and innovations made by enterprises themselves.
2. Problems
The Chinese and world experiences have suggested that for industries with the set-up cost unsolved, the development and innovation of the industrial chains call for government support. In present China, the industries requiring more policy support from the government are mainly those technology-intensive or knowledge-based industries that require huge investment and set high standards for market access as well as those widely open industries with the set-up cost unsolved where there is much difference in comprehensive capacity and technical competence between Chinese and foreign enterprises (Table 1). After the strength has been enhanced, those enterprises can create innovation of industrial chains fully on their own. For example, China Mobile and Huawei have realized the upgrading of China Mobile network by jointly developing the technically complicated IP network with huge investment, thus making Huawei one of the world's largest supplier of key IP network1.
Despite a high expectation among all walks of life for policies to be set out by the Chinese government,the specific characteristics and the roads taken by China for its development have made some people to be skeptical about and even worry about what a role the Chinese government could play in coordinating and promoting the innovation of the industrial chains. There is much difference between Chinese domestic enterprises and the enterprises of developed countries;it is imperative for China to provide backing for the enterprises to develop themselves and create innovations with resources or "rent chances" (or "performance-based rent") supplied by the government,but there exists a risk that the relationship between the government and the enterprises might be handled with measures left over from the traditional planned economy. Under the influence of "path dependence", China's reform and development, proceeding from the national conditions, are characterized by "extra-systematic reform and development" which stimulate the "systematic reform and development" as well as by opening-up which facilitates reform and development. It is a road of success with interactions and competitions from various sides and yet it restrains the government from deciding on policies and measures.
Table 1 Status of Relevant Industrial Chains
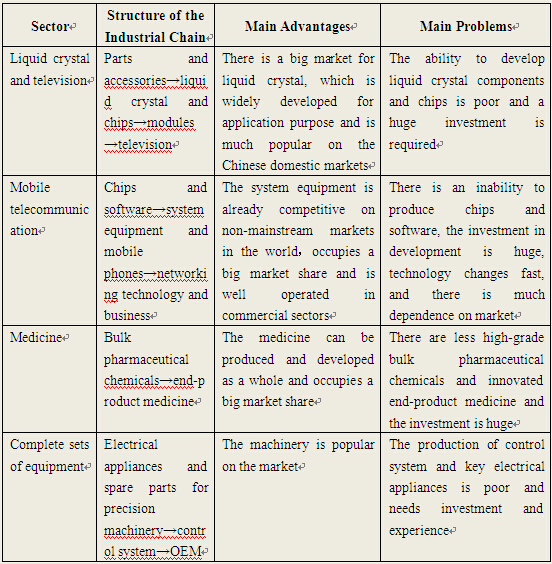
Note: A summarization of surveys by the authors.
Another critical restraint is that the international environment has made it difficult for China to follow the example of what Japan and the Republic of Korea had ever done. After the accession to WTO, China has opened wider to the outside world and, through investment and acquisition, the foreign companies have formed the advantages from "made in China by foreign companies". When the industrial chains of Chinese domestic enterprises are formed, there is much possibility for resources to become incompatible or even conflicting with each other.
…
If you need the full text, please leave a message on the website.
1For details about the co-operation between China Mobile and Huawei, see Chapter 6 of Mobile Telecommunication Revolution by Chen Xiaohong, Ma Jun & He Xia, Post and Telecommunications Press of Beijing University, 2007














