Analysis and Forecast of the Market Situationin the First Half of 2006*
Sep 11,2006
By Ren Xingzhou
Research Report No 176, 2006
I. Overall Situation of the Economic Operations in the First Half of 2006
1. Overall operation of the national economy
(1) The national economy continued to grow in a sustainable and rapid way
In the first half of 2006, China's national economy continued to grow in a sustainable and rapid way. A GDP worth of 9144.3 billion yuan was fulfilled, up 10.9% over the same period last year, which was the fastest in nearly 10 years. Of which, added value of the three industries rose 5.1%, 13.2% and 9.4% respectively, as compared with the same period of last year. In the first 6 months, industries above designated size throughout the country fulfilled an added value of 3968 billion yuan, up 17.7% over the same period of last year. Of which, heavy and light industries rose 18.5% and 15.8% respectively. Production went well with sales. The selling rate of the industrial products above designated size reached 97.4%. Increase in profits of the industrial enterprises speeded up. From January through May, industrial enterprises above designated size realized a profit of 629.4 billion yuan, up 25.5% over the same period last year, rising 9.7 percentage points as compared with the same period of last year. Agricultural production saw a good situation. Summer grain crops obtained harvest continually in the third year, with the total output reaching 113.8 billion kilograms, increasing by 7.4 billion kilograms, up 7.0% over the same period of last year.
(2) Growth of fixed asset investment accelerated
From January through June, growth of fixed asset investment accelerated evidently. Fixed asset investment of the whole society grew 29.8% over the same period last year, accelerating 4.4 percentage points. Of which, fixed asset investment in cities and towns grew 31.3% over the same period of last year, accelerating 4.2 percentage points (see Graph 1). In view of the structure, investment in real estate development grew 24.2% over the same period of last year, accelerating 0.7 percentage point. Investment in heavy industry grew 32.6% over the same period of last year, of which, investment in coal mining and ore dressing grew 45.7%, investment in oil and natural gas extracting grew 30.3%, investment in production and supply of electric power, gas and water grew 17.5%, investment in railway transportation grew 87.6%, and investment in light industry grew 41.2%.
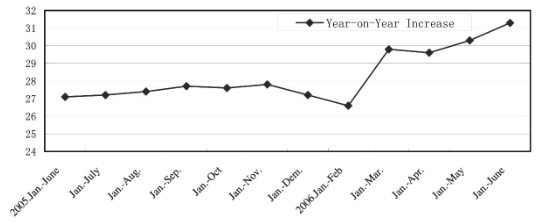
Graph 1 The Year-on-Year Growth of Fixed Asset Investment during the Latter Half of 2005 and the First Half of 2006
Source: China Economic Boom Monthly
(3) Incomes of the residents in urban and rural areas grew fast, and consumptive demands grew steadily
In the first half of the year, per-capita disposable income of the residents in cities and towns throughout the country amounted to 5997 yuan, with price factor being ruled out, actually rising 10.2%, with the increase showing 0.7 percentage points faster; per-capita cash income of the peasants amounted to 1797 yuan, actually rising 11.9%, falling back 0.6 percentage points after the rise.
Consumptive demands continued to grow steadily. In the first half of the year, the total retail value of social consumer goods amounted to 3644.8 billion yuan, up 13.3% over the same period of last year, with the price factor being ruled out, actually rising 12.4%, accelerating 0.4 percentage points as compared with the same period of last year. By trades and professions, retail value of the wholesale and retail industries amounted to 3082.1 billion yuan, up 13.4%; retail value of lodging and catering industries amounted to 492.9 billion yuan, up 15.3% (see Graph 2).
(4) CPI continued to rise in a mild way, and PPI kept a rising momentum
In the first half of the year, the aggregate level of CPI rose 1.3%, reducing 1 percentage point over the same period of last year; the month-on-month price index increased by 0.5%. From January through June, food price and housing price rose 1.9% and 4.7% respectively as compared with the same period of last year, which were the main factors to result in the rise of CPI. In the first half of the year, retail commodity prices rose 0.8% over last year; producer prices of industrial products rose 2.7% over last year; purchase prices of raw materials, fuel and motive power rose 6.1% as compared with the same period of last year.
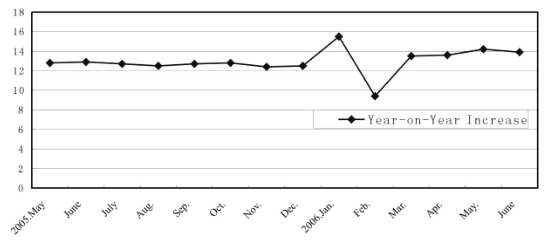
Graph 2 Increase of the Total Retail Value of Social Consumer Goods from May 2005 to June 2006
Source: sorted out according to China Economic Boom Monthly
What is worth noticing in CPI change in the first half of the year is that the conductivity of the resource prices to commodity and service prices was increasingly obvious. In the first half of the year, due to the influence of the increase in world oil prices, the state twice raised prices of oil products, and prices of other resources rose in varying degrees. As about half of the increase in service prices came from the conduction of resource prices, and the rise of resource prices inevitably brought about the overall rising of the service prices, thus leading to the increase of CPI directly or indirectly.
(5) Housing prices remained high, and prices in some cities grew excessively high
In the first half of 2006, sales prices of houses in 70 large and medium-sized cities rose 5.6% over the same period of last year, falling back 3.3 percentage points after the rise; in the second quarter, increase of the sales prices of the newly-built commercial housing began to bounce back, with the aggregate level remaining high. In the first 5 months, sales prices of the second-hand houses throughout the country rose steadily, with an increase of 4.9% in June, showing a fall after the rise, which suggested the response of the market to the macro-control policy put out at the end of May. House leasing prices rose 1.6% in the second quarter as compared with the same period of last year, up 0.5 percentage points as compared with the first quarter.
In the first half of the year, housing prices in some cities grew fast. Among 70 large and medium-sized cities across the country, prices of the newly-built residences in 23 cities had surpassed the country's average in June, of which prices of the newly-built residences in Shenzhen and Beijing rose 14.6% and 11.2% respectively over the same period of last year, up 5 percentage points as compared with July of last year. In June, prices of the ordinary residences in Shenzhen rose 18.94%; prices of the ordinary houses in Beijing grew 1.3 percentage points higher than commercial housing prices.
(6) Monetary credit showed a momentum of excessively rapid growth
The first half of the year saw a financial situation of "easy money, easy credit ". By the end of June, the broad money (M2) increased 18.4% over the same period last year, accelerating 2.7 percentage points as compared with the same period last year, with the increase being the fast in recent years. The narrow money (M1) increased 13.9%, accelerating 2.7 percentage points over the same period last year; cash in circulation (M0) rose 12.6%, accelerating 2.9 percentage points over the same period of last year.
In the first half of the year, the newly-increased RMB loans amounted to 2170 billion yuan, equivalent to 1.5 times of the newly-increased loans in the same period of last year, reaching 85.9% of the expected controlling target of 2500 billion yuan for the whole year of 2006 ( see Graph 3 ). Under such circumstances, the mobility of the banking system was made to be excessively loose, thus further leading to the rapid growth of the fixed asset investment.
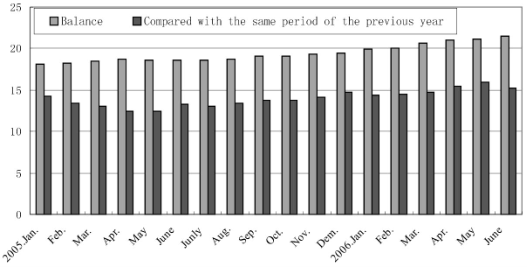
Graph 3 Changes in Balance of RMB Loans During 2005 – 2006
Source: sorted out according to the data released by the People's Bank of China.
…
If you need the full text, please leave a message on the website.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*The present paper is the general report of " Analysis of the Chinese Market Situation in the First Half of 2006 and Forecast of the Latter Half of the Year " provided by the Institute of Market Economy.














