Cellular endothelial microRNA-483 significantly inhibits pulmonary hypertension
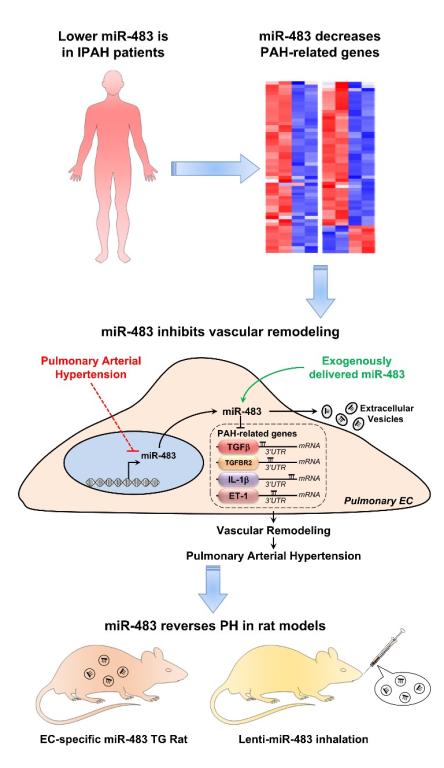
“Lower levels of microRNA-483were found in serum from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH), particularly those with more severe disease.” This result was found by a research team from the School of Basic Medical Sciences, XJTU Health Science Center. RNA-seq and bioinformatics analyses showed that microRNA-483 targets several PAH-related genes, including transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β), TGF-βreceptor 2 (TGFBR 2), β-catenin, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), interleukin-1β(IL-1β), and endothelin-1 (ET-1). Results indicate that endogenous or exogenous overexpression of microRNA-483 in endothelial cells significantly inhibits pulmonary hypertension, providing new possible target points and an experimental basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
The results were published inEMBO Molecular Medicinetitled MicroRNA‐483 amelioration of experimental pulmonary hypertension, with XJTU’s doctoral candidate, Zhang Jin, the first author, and XJTU the institutional affiliation of the first author.

