
- Home
- Media Center
-
Events
- Wuzhen Summit
- Regional Forums
- Practice Cases of Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace
- World Internet Conference Awards for Pioneering Science and Technology
- The Light of Internet Expo
- Straight to Wuzhen Competition
- Global Youth Leadership Program
- WIC Distinguished Contribution Award
- Membership
- Research & Cooperation
- Digital Academy
-
Reports
- Collection of cases on Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace
- Collection of Shortlisted Achievements of World Internet Conference Awards for Pioneering Science and Technology
- Reports on Artificial Intelligence
- Reports on Cross—Border E—Commerce
- Reports on Data
- Outcomes of Think Tank Cooperation Program
- Series on Sovereignty in Cyberspace Theory and Practice
- Other Achievements
- About WIC
- 中文 | EN

Beijing unveils high-tech air monitoring system
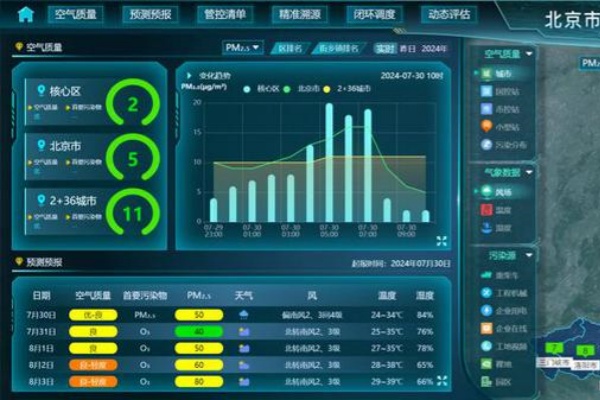
Beijing has implemented an innovative Supervision-Monitoring-Inspection (SMI) mechanism to drive air pollution control toward scientific, precise, and efficient development. [Photo provided to chinadaily.com.cn]
Beijing has implemented an innovative Supervision-Monitoring-Inspection (SMI) mechanism to drive air pollution control toward scientific, precise, and efficient development, the Beijing Municipal Ecology and Environment Bureau said at a press conference on Tuesday.
The SMI mechanism involves coordinated supervision by regulatory administrations, intelligent perception by monitoring administrations, and precise enforcement by inspection authorities.
The bureau has developed a large-scale model to support the SMI mechanism, utilizing big data and artificial intelligence.
This model, supported by a new monitoring network, intelligent analysis techniques, and an efficient dispatching system, robustly enhances the operation of the SMI mechanism, advancing the modernization of air pollution control capabilities.
The bureau has upgraded the traditional monitoring system by employing sensors, the Internet of Things (IoT), and remote satellite sensing technology, creating a new generation of monitoring systems. It provides substantial data support and governance clues for the SMI mechanism.
Remote satellite sensing can intelligently identify over 10 types of targets, including bare land and black-odor water, with an accuracy rate of 90 percent.
Mobile monitoring vehicles patrol the ground, measuring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in real-time, achieving second-level response, intelligent traceability, and closed-loop regulation.
By integrating economic and social operation data, such as electricity consumption and construction site records, into the ecological environment monitoring network and analyzing it with intelligent algorithms, comprehensive and real-time monitoring of various pollution sources is realized.
Given the city's low air pollution levels, Beijing has built an intelligent recognition algorithm library, developing 26 types of algorithms to identify issues like vehicle emission exceedance. These algorithms dynamically track high-value emissions, excessive discharges, and violations.
The SMI tri-mechanism has significantly supported continuous improvement in air quality. In Beijing, the concentration of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) dropped from 38 micrograms per cubic meter in 2020 to 32 micrograms per cubic meter in 2023, meeting the national air quality standards for a third consecutive year.

The World Internet Conference (WIC) was established as an international organization on July 12, 2022, headquartered in Beijing, China. It was jointly initiated by Global System for Mobile Communication Association (GSMA), National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China (CNCERT), China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC), Alibaba Group, Tencent, and Zhijiang Lab.





