Tibet Before the Peaceful Liberation
Updated: 2021-05-21 (Xinhua)  Print
Print 

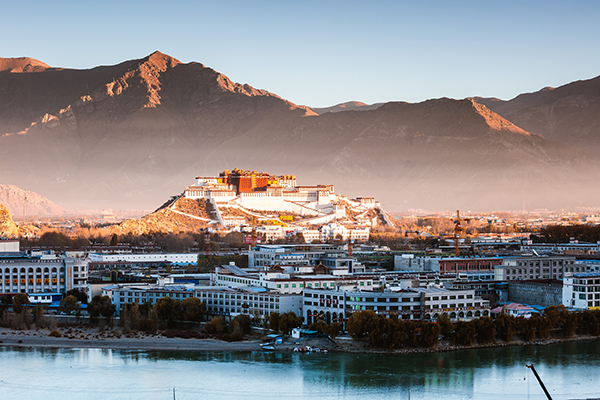
Tibet has been an integral part of Chinese territory since ancient times, and one of the main Tibetan-inhabited areas in China. In the aftermath of the Opium Wars in the middle of the 19th century, the UK-led imperialist powers began to cultivate the idea of "Tibet independence", intentionally undermining China's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
– Tibet has been an inseparable part of China since ancient times.
China is a unified multiethnic country with a long history. The Chinese nation is a community of shared future. Tibet has developed through the combined efforts of all the ethnic groups in China, and these are the peoples who have created its history. The political, economic and cultural exchanges between Tibetans and other ethnic groups throughout history have had an important bearing on the development of the Tibetan people as an ethnic group. Abundant archeological and academic research shows that in times of remote antiquity, the ancestral people inhabiting the Tibetan Plateau had close ties with the Han and other ethnic groups in terms of blood, language, and culture. The Tubo Kingdom established in Tibet in the 7th century contributed significantly to the exploration of China's southwestern borders.
In the Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368), the central government exercised jurisdiction and governance over Tibet. It established the Supreme Control Commission of Buddhism (later renamed the Commission for Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs) to directly manage local affairs in the region, conducting censuses, setting up courier stations, collecting taxes, stationing troops and appointing officials. It also issued and enacted the Yuan criminal law and calendar in Tibet.
The central government of the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) implemented a policy of multiple enfeoffment, conferring honorific titles such as "Prince", "Prince of Dharma", and "National Master in Tantrism" on political and religious leaders in various parts of Tibet. It established the U-Tsang and Do-kham regional military commissions and the Ngari Commanding Tribal Office to manage military and political affairs in U-Tsang, Qamdo and Ngari respectively.
During the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), the central government exercised sound governance over Tibet. It granted honorific titles to the leaders of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism – the 5th Dalai Lama and the 5th Panchen Lama – officially establishing the titles of the Dalai Lama and Panchen Erdeni and their political and religious status in Tibet. From then on, it became an established convention that the central government conferred the titles of Dalai Lama and Panchen Erdeni. The Qing government began to station Grand Ministers Resident in Tibet to supervise and jointly manage local military and political affairs on behalf of the central authorities; in total it appointed more than 100 such ministers. In 1751, Qing Emperor Qianlong authorized the 7th Dalai Lama to jointly manage local political and religious affairs with the Grand Minister Resident in Tibet. In 1793, after dispelling Gurkha invaders, the Qing government restored order in Tibet and promulgated the Imperially Approved Ordinance for Better Governance of Tibet (the 29-Article Ordinance), improving several of the systems by which the central government administered Tibet. The ordinance stipulated that the reincarnation of the Dalai Lama and other grand Living Buddhas had to follow the procedure of "drawing lots from the golden urn", and the selected candidate would be subject to approval by the central government of China. Observing the ordinance, three of the five Dalai Lamas in the Qing Dynasty were selected and approved in accordance with this procedure, and the other two were exempted from the procedure with special approval from the central government.
After the downfall of the Qing Dynasty, the Republic of China (ROC) continued to exercise sovereignty over Tibet. In 1912, the ROC issued its first constitution – the Provisional Constitution of the Republic of China, which reaffirmed the central government's sovereignty over Tibet. It clearly stipulated that "Tibet is a part of the territory of the ROC", and stated that "the Han, Manchu, Mongol, Hui and Tibetan peoples are of one nation, and are to run the Republic together." In July, the government set up the Bureau of Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs. The Nanjing National Government set up the Commission for Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs in 1929 to act in the same capacity. In 1940, the Commission for Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs opened an office in Lhasa as the permanent organ representing the central government in Tibet. Under the ROC, Tibet was clearly identified as Chinese territory in world maps and maps of China issued by government and non-government publishers. The central government of the ROC safeguarded the nation's sovereignty over Tibet in spite of frequent civil wars among warlords and a weak state, and following the tradition by conferring the official titles on the 14th Dalai Lama and the 10th Panchen Lama. No country or government in the world has ever acknowledged the "independence of Tibet".
– "Tibetan independence" was a product of imperialist aggression against China in modern times.
Western attempts on Tibet began in the 18th century, pioneered by "adventurers" and "explorers" who made trips to the region. At the end of the 19th century, imperialist powers engaged in a fervent spree of carving up China, and the British aggressors took the opportunity to invade Tibet. British troops invaded Tibet twice in 1888 and 1903 and met with stubborn resistance from the Tibetan army and civilians. Its invasion plans thwarted, Britain began to cultivate pro-imperialist separatists in Tibet, devising activities to separate Tibet from China and championing "Tibet independence". In 1907, Britain and Russia signed the Convention Between Great Britain and Russia on Tibet, without the Chinese government's knowledge, changing China's sovereignty over Tibet into "suzerainty" in an international document for the first time. In 1913, the British government engineered the Simla Conference to instigate the Tibetan representative to raise the issue of "Tibetan independence", which was immediately rejected by the representative of the Chinese government. This was the first time the concept had been made public. In July 1914, the representative of the Chinese government refused to sign the Simla Convention, and made a statement saying that the government of China refused to recognize any such agreement or document. The Chinese government also sent a note to the British government, reiterating its position. Thereupon, the conference collapsed.
In 1942, the local government of Tibet, with the support of the British representative, suddenly announced the establishment of a "foreign affairs bureau" and began to openly engage in "independence" activities. With opposition from the Chinese people and the national government, the local government of Tibet had no choice but to withdraw its decision. In 1947, Britain conspired behind the scenes to invite Tibetan representatives to attend the Asian Relations Conference, and even identified Tibet as an independent country on the map of Asia hung in the conference hall and in the array of national flags. The organizers were forced to rectify this after the Chinese delegation made a stern protest.
Around the time of the founding of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949, imperialists accelerated their collusion with pro-imperialist separatists in Tibet. On July 8, 1949, the local government of Tibet issued an order to expel officials of the Tibet Office of the Commission for Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs on the pretext of "prohibiting Communists from staying in Tibet". In November 1949, the local government of Tibet decided to dispatch a "goodwill mission" to the United States, Britain, India, Nepal and a number of other countries, seeking political and military support for "independence" and making it obvious that it was intensifying separatist activities. In 1949, the American Lowell Thomas crossed Tibet in the guise of a "radio commentator" of the Columbia Broadcasting System to explore the "possibility of aid that Washington could give Tibet". He wrote in a US newspaper: "The United States is ready to recognize Tibet as an independent and free country." In the first half of 1950, American weaponry was shipped into Tibet through Calcutta in order to help resist the People's Liberation Army's entry into Tibet.
Historical facts clearly demonstrate that "Tibetan independence" was no more than a product of imperialist aggression against China. Driving imperialist forces out of Tibet was the precondition for the Chinese people to safeguard national unification.
– Liberating Tibet was the shared aspiration of all ethnic groups in Tibet.
On September 2, 1949, Xinhua News Agency, with authorization from the CPC, published an editorial under the headline, "Foreign Aggressors Are Resolutely Not Allowed to Annex China's Territory – Tibet". The editorial pointed out, "Tibet is part of the Chinese territory; no foreign aggression is allowed. The Tibetan people are an inseparable part of the Chinese nation, and any attempt to divide them from China will be doomed. This is a consistent policy of the Chinese people, the CPC and the People's Liberation Army (PLA)."
All sectors of society of Tibet quickly responded and expressed support for the editorial and the hope that the PLA would enter Tibet as soon as possible. On October 1, 1949, the day the PRC was founded, the 10th Panchen Lama sent a telegram to the central government: "Please send troops to liberate Tibet and expel the imperialists as soon as possible."
On December 2, Yeshe Tsultrim, an aide of the 5th Regent Reting Rinpoche, arrived in Xining, Qinghai Province, to lodge complaints with the PLA about the imperialists destroying the internal unity of Tibet, and urged the PLA to liberate Tibet as soon as possible.
Sherab Gyatso, a prominent Tibetan scholar, delivered a talk in Xi'an, denouncing an imperialist conspiracy through which Lhasa authorities would seek "independence". In early 1950, over 100 Tibetan people, including farmers and herdsmen, young people, women and democratic representatives, assembled in Lanzhou in Gansu Province, which had been liberated not long before, and urged the PLA to liberate Tibet.
In their reply to the 10th Panchen Lama, Mao Zedong and Zhu De stated, "The Tibetan people love the motherland and stand against foreign aggression. They are discontent with the policies of the reactionary Kuomintang government, and want to be part of the big family of a unified New China, where all ethnic groups are equal and work together for prosperity. The Central People's Government and the Chinese PLA will certainly comply with this wish of the Tibetan people."
With determined support from the Central People's Government, Tibet saw the hope of a peaceful liberation anticipated by the whole of China.








