Indicators reveal sound economic recovery momentum in H1
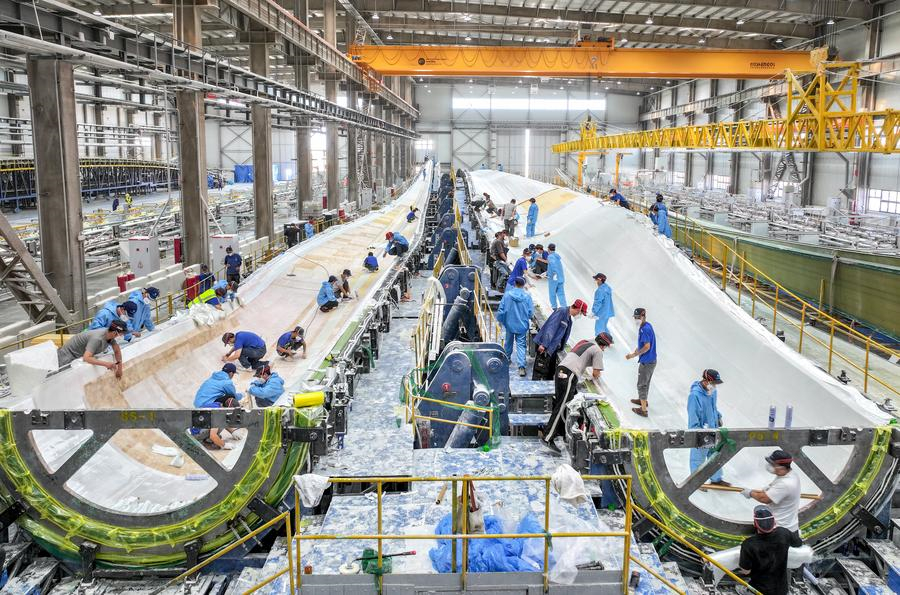

An aerial drone photo taken on May 11, 2024 shows workers working at a wind power equipment manufacturer in Baotou, north China's Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. [Xinhua/Lian Zhen]
BEIJING -- Recently released indicators point to continuous, solid momentum in China's economy during the first half of the year, building confidence in a broader recovery.
The June purchasing managers' index (PMI) for China's manufacturing sector, a gauge of the vitality of manufacturing activities, was unchanged from May, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS).
Notably, the high-tech manufacturing reading remained in the expansion range for an eighth consecutive month, rising from 50.7 in May to 52.3 in June. The equipment manufacturing reading was 51, remaining in expansion territory for a fourth successive month.
Wen Tao, an analyst at the China Logistics Information Center, highlighted that the June sub-index performance indicates accelerated production, the burgeoning development of new growth drivers, enhanced vitality within microeconomic entities, and alleviated pressure from raw material costs.
The average PMI in the first half of 2024 was 49.8, a 0.3 percentage- point increase from the second half of 2023, indicative of a sustained economic recovery trend, according to Wen.
China's economic sustainability has also been reflected in the operations of industrial firms. Earlier NBS data shows that China's major industrial firms saw their combined profits reach 2.75 trillion yuan (about 385.88 billion U.S. dollars) during the January-May period, a 3.4 percent year-on-year increase.
Zhang Liqun, a researcher at the Development Research Center of the State Council, has attributed the upward momentum to the effectiveness of policies aimed at stabilizing growth and promoting recovery.
Zhang also highlighted the importance of bolstering countercyclical macroeconomic policy adjustments, stressing that China currently stands at a pivotal juncture for advancement amid adversity.
Despite its ongoing economic recovery, China continues to face numerous challenges on both domestic and international fronts, including a complex and uncertain external environment, inadequate effective demand, and weak public expectations.
Against this backdrop, the world's second-largest economy has devised and implemented a series of pro-growth policies to enhance economic resilience and foster sustainable growth, alongside efforts to achieve its target GDP growth rate of approximately 5 percent this year.
In one such policy move, China has announced the issuance of 1 trillion yuan of ultra-long special treasury bonds, a rarely used fiscal tool, to support the implementation of major national strategies and enhance security capacities in key areas.
As of June 14, four batches of these bonds have been issued since May, with the remaining bonds scheduled for issuance by mid-November, according to the Ministry of Finance.
China has also offered robust financial support to facilitate large-scale equipment renewal and consumer goods trade-ins. In April, the country established a re-lending program worth 500 billion yuan to promote technological innovation and industrial upgrades, designating 100 billion yuan to boost the growth of tech firms specifically.
According to a China Merchants Bank research institute, these policy initiatives will play an important role in fueling domestic demand. Investment in manufacturing equipment is set to increase from last year by approximately 300 billion yuan in 2024, potentially driving up overall manufacturing investment by 1 percent, according to a rough estimate from the institute.
In shoring up consumption, the National Development and Reform Commission, the country's top economic planner, along with three other government bodies, unveiled measures in late June to create new consumption scenarios in multiple sectors, including tourism, automobiles and electronics.
Under the new measures, China will expand its visa-free transit policy, relax vehicle purchase restrictions, and spur the consumption of intelligent, AI-powered electronics.
Looking ahead, Zhang Wenlang, chief macro analyst at China International Capital Corporation Limited Research, anticipates the pace of fiscal expenditure in the second half of 2024 will outpace that of the first half.
"Underpinned by a robust export performance, the economy is expected to maintain stability in the latter half of the year, accompanied by a slight increase in inflation," Zhang said in a research note.
"As policies are implemented with greater precision, their effectiveness will be realized fully, offering sustained support for the development of the real economy," said Liu Aihua, NBS spokesperson.